[콜라츠 추측] 파이썬 GUI로 콜라츠 추측 알아보기1
콜라츠 추측에 대해서 들어보셨나요? 콜라츠 추측이란 임의의 양의 정수 n에 대해서 홀수 일 경우 3*n + 1을 하고 짝수일 경우 n / 2를 하는데 이를 임의의 양의 정수에 수행하면 항상 마지막은 4 2 1
c-i-s.tistory.com
해당 포스팅에 이어지는 내용입니다.
우선 gui로 표현하기 위해 공간을 만들어보겠습니다.
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title("콜라츠 추측")
root.geometry("1600x800+100+100")
root.mainloop()-> 가로 1600, 세로 800입니다.
-> 프로그램의 등장 위치는 좌 상단으로 부터 가로 100 세로 100 떨어진 위치에 나옵니다.
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title("콜라츠 추측")
root.geometry("1600x800+100+100")
canvas = Canvas(root, width=1600, height=700, background="#ffffff")
canvas.place(x=0, y=0)
root.mainloop()실행 결과

-> 뭔가 그리기 위해서 Canvas 위젯을 만들어 줍니다.
-> 캔버스의 배경색은 흰색, 가로 크기 1600, 세로 크기 700
-> 남는 100은 여러가지 설정이 들어갈 예정입니다.
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title("콜라츠 추측")
root.geometry("1600x800+100+100")
canvas = Canvas(root, width=1600, height=700, background="#ffffff")
canvas.place(x=0, y=0)
# x축 y축 그리기
# 먼저 x축 부터
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 1550, 650, fill="#000000")
Label(canvas, text="x축", background="#ffffff").place(x=1400, y=660) # x축 표시
# 그 다음 y축
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 50, 50, fill="#000000")
Label(canvas, text="y축", background="#ffffff").place(x=20, y=80)
# 원점 표시
Label(canvas, text="원점", background="#ffffff").place(x=30, y=660)
root.mainloop()실행 결과

-> x축 y축 원점을 표시해보았습니다.
이제 임의의 자연수를 받을 입력창을 만들겠습니다.
from tkinter import *
def push():
pass
root = Tk()
root.title("콜라츠 추측")
root.geometry("1600x800+100+100")
canvas = Canvas(root, width=1600, height=700, background="#ffffff")
canvas.place(x=0, y=0)
# x축 y축 그리기
# 먼저 x축 부터
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 1550, 650, fill="#000000")
Label(canvas, text="x축", background="#ffffff").place(x=1400, y=660) # x축 표시
# 그 다음 y축
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 50, 50, fill="#000000")
Label(canvas, text="y축", background="#ffffff").place(x=20, y=80)
# 원점 표시
Label(canvas, text="원점", background="#ffffff").place(x=30, y=660)
# 임의의 자연수
Label(root, text="natural_number:", font=('consolas', 20)).place(x=50, y=730)
natural_number = Entry(root, width=20, font=('consolas', 18))
natural_number.place(x=280, y=735)
# 버튼 만들기
Button(root, text="draw", font=('consolas', 18), command=push).place(x=580, y=727)
root.mainloop()실행 결과
-> draw 버튼을 누르면 그래프를 그리기 시작합니다.
-> 아직 그리는 코드가 없습니다.
-> 그리기 위해서 우선 좌표 정보를 가져오도록 하겠습니다.
def push():
global natural_number
num = int(natural_number.get())
pos_list = []
while num != 1:
if num % 2 == 0:
num = int(num / 2)
pos_list.append(num)
else:
num = num * 3 + 1
pos_list.append(num)
-> 아까 pass가 있던 push 함수입니다.
-> 버튼을 클릭하면 이 함수가 동작이 되는데 x축은 일정하니까 안 구해도 돼고 y축 좌표 리스트를 구하는 과정입니다.
def push():
global natural_number, canvas
num = int(natural_number.get())
pos_list = []
while num != 1:
if num % 2 == 0:
num = int(num / 2)
pos_list.append(num)
else:
num = num * 3 + 1
pos_list.append(num)
x = 50
for i in range(len(pos_list)-1):
canvas.create_line(x, pos_list[i], x+10, pos_list[i+1])
x += 10실행 결과
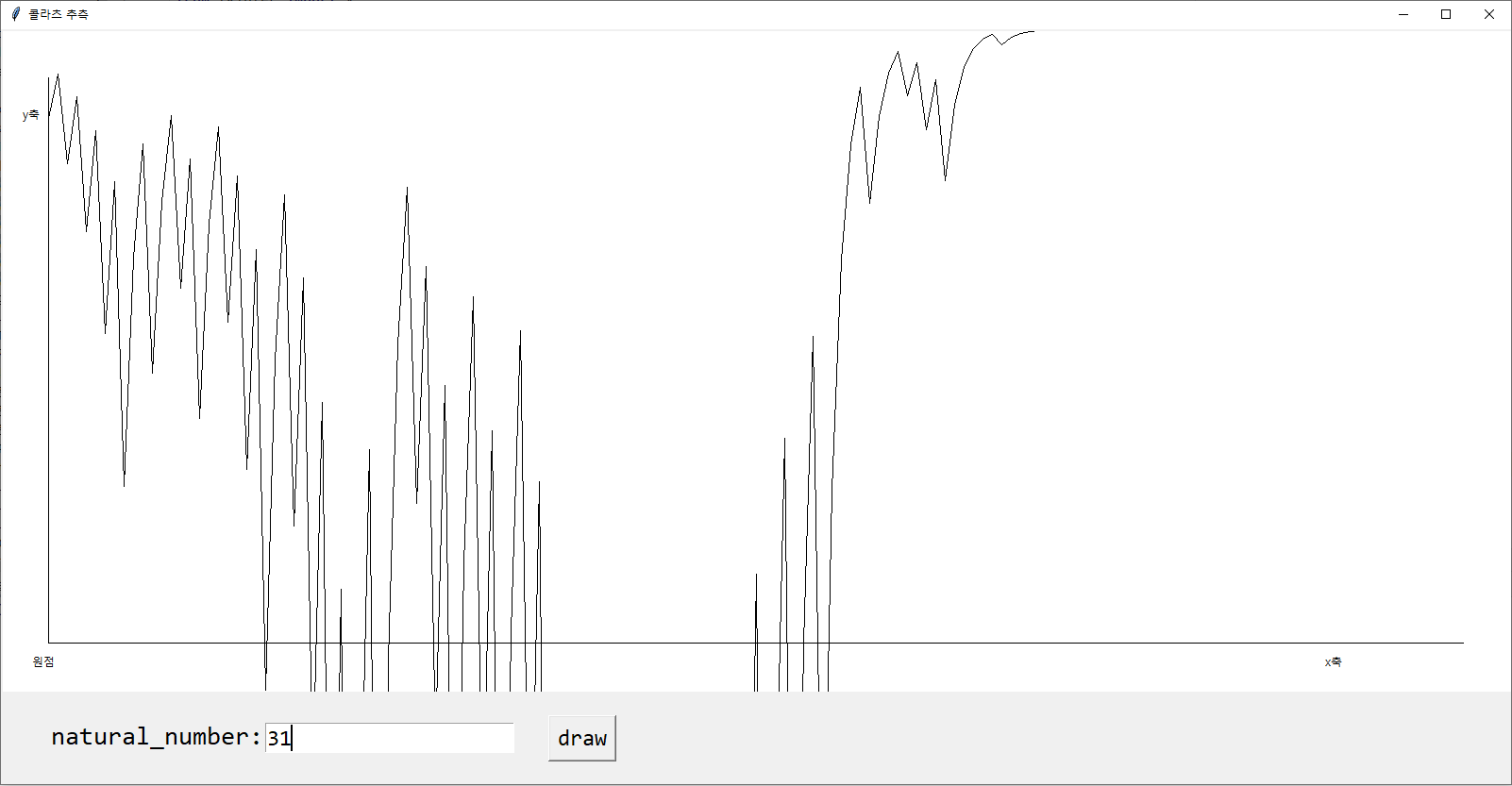
-> 그래프가 이상합니다
-> 이상한 이유는 tkinter의 좌표체계가 우리가 일상적으로 아는 좌표체계가 아니기 때문입니다.
-> 화면의 좌측 상단이 (0, 0)이기 때문에 좌표를 맞춰줘야 합니다.
-> 때문에 for문을 아래와 같이 변경할 수 있습니다.
for i in range(len(pos_list)-1):
canvas.create_line(x, -pos_list[i]+650, x+10, -pos_list[i+1]+650)
x += 10-> -pos_list[i] + 650 을 한 이유는 좌표를 반전 시킨 것입니다.
x = 50
k = 20 # y축 비례 변환
for i in range(len(pos_list)-1):
canvas.create_line(x, -pos_list[i]/k+650, x+10, -pos_list[i+1]/k+650)
x += 10
Label(canvas, text=str(pos_list[i]), font=('consolas', 7)).place(x=20, y=-pos_list[i]/k+650)실행 결과입니다.
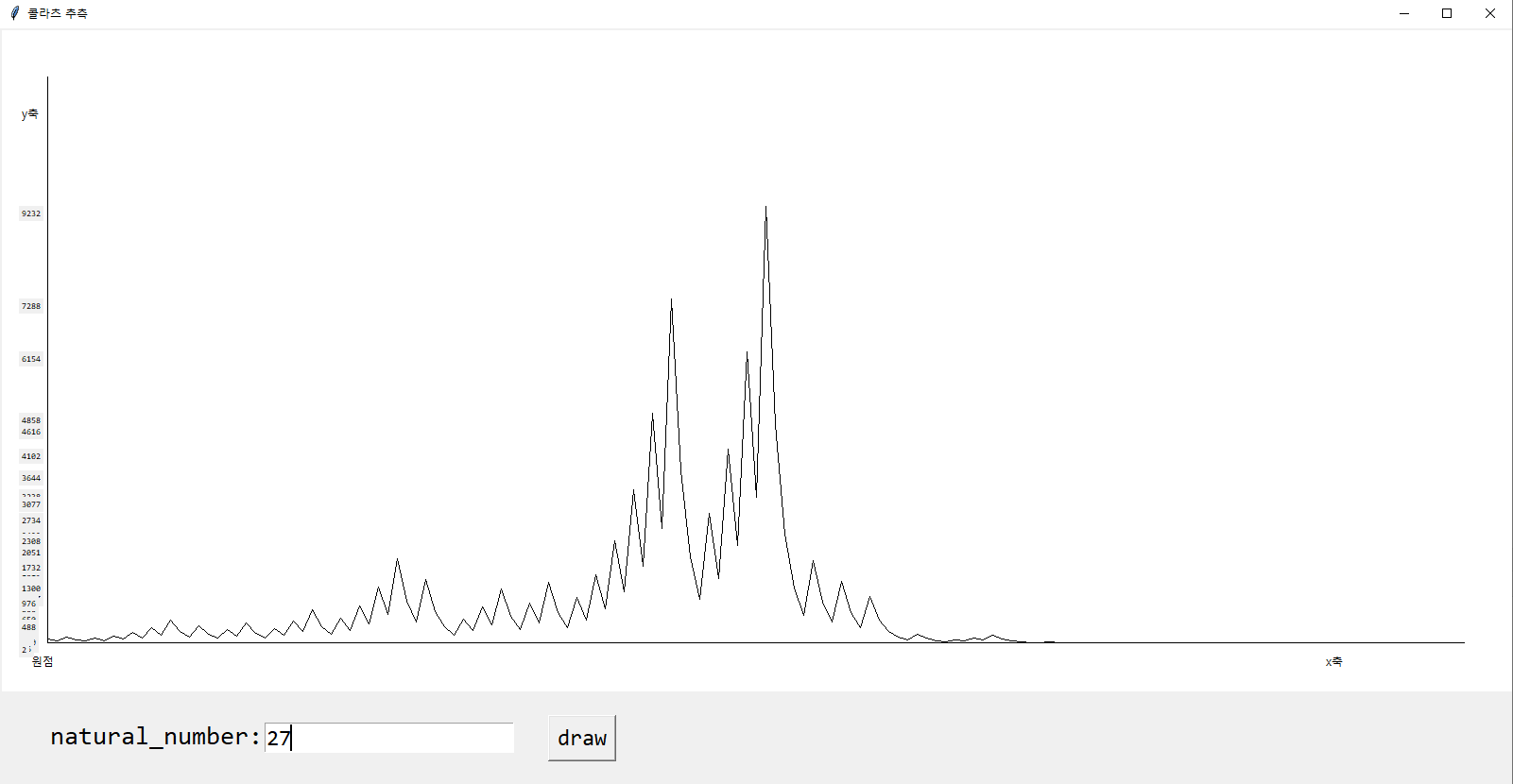
잘 나오는 것을 보실 수 있습니다.
y축 비례 변환을 할 수 있는 Entry 위젯도 만들어보겠습니다.
from tkinter import *
def push():
global natural_number, canvas, proportion
num = int(natural_number.get())
pos_list = []
while num != 1:
if num % 2 == 0:
num = int(num / 2)
pos_list.append(num)
else:
num = num * 3 + 1
pos_list.append(num)
x = 50
k = int(proportion.get()) # y축 비례 변환
for i in range(len(pos_list)-1):
canvas.create_line(x, -pos_list[i]/k+650, x+10, -pos_list[i+1]/k+650)
x += 10
Label(canvas, text=str(pos_list[i]), font=('consolas', 7)).place(x=20, y=-pos_list[i]/k+650)
root = Tk()
root.title("콜라츠 추측")
root.geometry("1600x800+100+100")
canvas = Canvas(root, width=1600, height=700, background="#ffffff")
canvas.place(x=0, y=0)
# x축 y축 그리기
# 먼저 x축 부터
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 1550, 650, fill="#000000")
Label(canvas, text="x축", background="#ffffff").place(x=1400, y=660) # x축 표시
# 그 다음 y축
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 50, 50, fill="#000000")
Label(canvas, text="y축", background="#ffffff").place(x=20, y=80)
# 원점 표시
Label(canvas, text="원점", background="#ffffff").place(x=30, y=660)
# 임의의 자연수
Label(root, text="natural_number:", font=('consolas', 20)).place(x=50, y=730)
natural_number = Entry(root, width=20, font=('consolas', 18))
natural_number.place(x=280, y=735)
# 버튼 만들기
Button(root, text="draw", font=('consolas', 18), command=push).place(x=580, y=727)
# y축 비례 변환하는 입력창
Label(root, text="y축 비례 변환:", font=('consolas', 20)).place(x=700, y=730)
proportion = Entry(root, width=7, font=('consolas', 18))
proportion.place(x=900, y=735)
root.mainloop()실행 결과입니다.
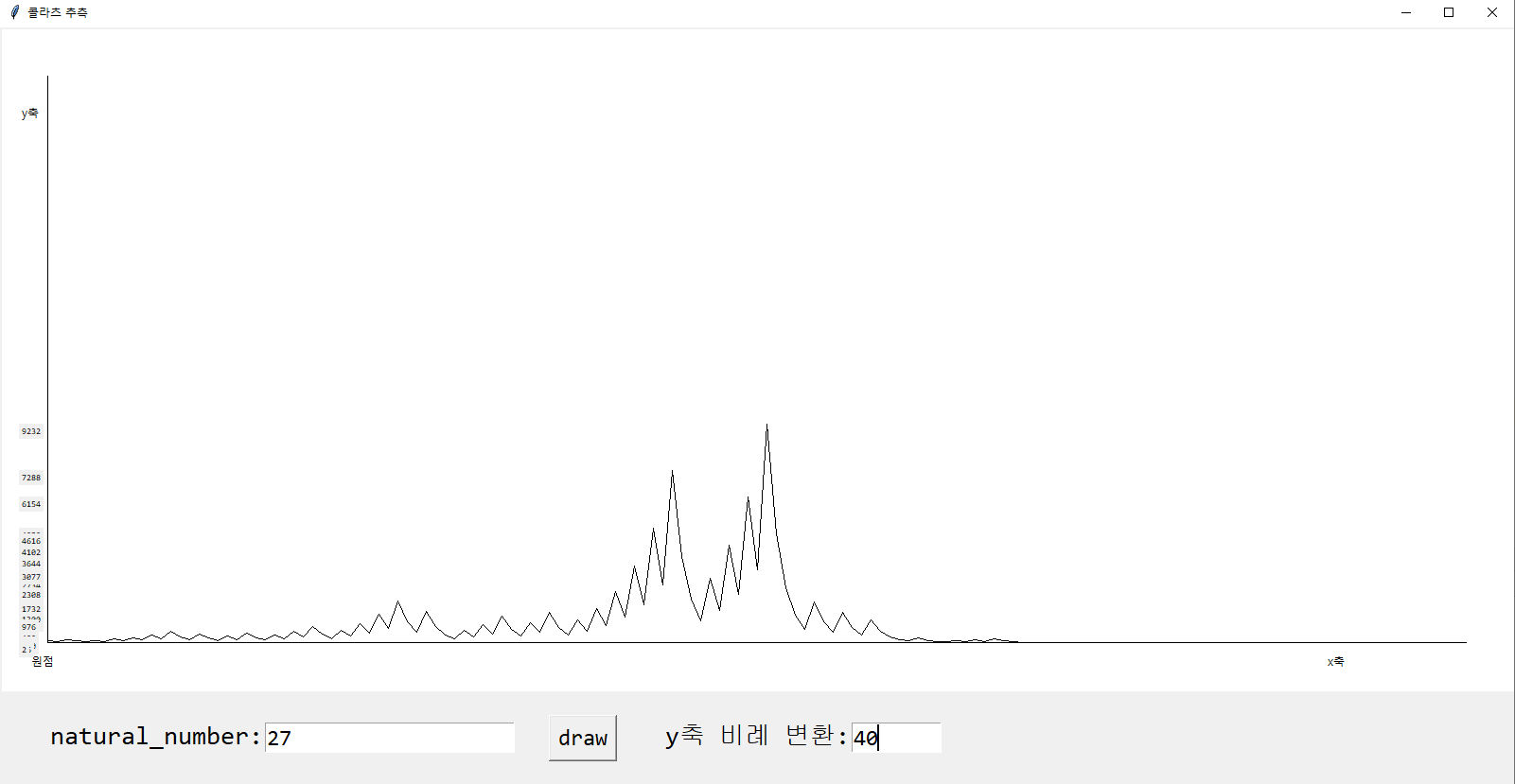
-> 변환된 값에 따라서 그래프의 높이가 다르게 보일 것입니다.
이제 지우는 버튼 만들어보도록 하겠습니다.
def clear():
global canvas
canvas.delete(ALL) # 캔버스로 그린 그림, 글자는 싹다 지워버리는 것입니다.# clear 버튼
Button(root, text="clear", font=('consolas', 18), command=clear).place(x=1500, y=727)-> 이걸 실행하면 모든 캔버스로 그림 것들이 지워집니다.
-> 근데 x축 y축도 같이 지워집니다.
-> 때문에 x축, y축 그리는 코드를 함수로 만들어서 재활용해보겠습니다.
from tkinter import *
def push():
global natural_number, canvas, proportion
num = int(natural_number.get())
pos_list = []
while num != 1:
if num % 2 == 0:
num = int(num / 2)
pos_list.append(num)
else:
num = num * 3 + 1
pos_list.append(num)
x = 50
k = int(proportion.get()) # y축 비례 변환
for i in range(len(pos_list)-1):
canvas.create_line(x, -pos_list[i]/k+650, x+10, -pos_list[i+1]/k+650)
x += 10
canvas.create_text(20, -pos_list[i]/k+650, text=str(pos_list[i]), font=('consolas', 7))
def clear():
global canvas
canvas.delete(ALL) # 캔버스로 그린 그림, 글자는 싹다 지워버리는 것입니다.
line()
def line():
global canvas
# x축 y축 그리기
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 1550, 650, fill="#000000") # x
canvas.create_line(50, 650, 50, 50, fill="#000000") # y
root = Tk()
root.title("콜라츠 추측")
root.geometry("1600x800+100+100")
canvas = Canvas(root, width=1600, height=700, background="#ffffff")
canvas.place(x=0, y=0)
Label(canvas, text="x축", background="#ffffff").place(x=1400, y=660) # x축 표시
Label(canvas, text="y축", background="#ffffff").place(x=20, y=80) # y축 표시
Label(canvas, text="원점", background="#ffffff").place(x=30, y=660) # 원점 표시
line() # 라인 그리기
# 임의의 자연수
Label(root, text="natural_number:", font=('consolas', 20)).place(x=50, y=730)
natural_number = Entry(root, width=20, font=('consolas', 18))
natural_number.place(x=280, y=735)
# 버튼 만들기
Button(root, text="draw", font=('consolas', 18), command=push).place(x=580, y=727)
# y축 비례 변환하는 입력창
Label(root, text="y축 비례 변환:", font=('consolas', 20)).place(x=700, y=730)
proportion = Entry(root, width=7, font=('consolas', 18))
proportion.place(x=900, y=735)
# clear 버튼
Button(root, text="clear", font=('consolas', 18), command=clear).place(x=1500, y=727)
root.mainloop()-> 최종적으로 완성이 되었습니다. x축이 길어서 x축도 비례 변환하는 것도 만들 수 있지만 굳이 그것까지 해야하나 싶습니다.
-> 단순히 퍼가도 좋지만 이해하면서 따라올 수 있도록 최대한 천천히 각 기능별로 나누어서 만들어보았습니다. 긴 글 읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
'프로그래밍 > 문제 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [콜라츠 추측] 파이썬 GUI로 콜라츠 추측 알아보기1 (0) | 2022.11.03 |
|---|---|
| [100명의 죄수 문제] 파이썬으로 확률 알아보기 (0) | 2022.10.07 |
댓글